Bracts, Bracteoles and Inflorescence
Bracts are morphologically specialised leaves from the axil of which flowers either solitary or in clusters (on floral axis) are developed.
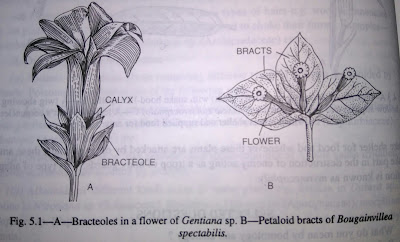 |
| A-bracteoles, B- petaloid bracts |
Bracteoles are smaller than bracts, either thin leafy or scaly structures developing on flower stalks in between bracts and calyx.
Types of Bracts : Bracts may be of different types as follows :
 |
| Types of bracts |
(a) Leafy or Foliaceous bracts-When bracts are typically and ordinarily green foliage leaf-like e.g. Hibiscus sp. (Malvaceae), Acalypha indica (Euphorbiaceae) etc.
(b) Petaloid bracts-When bracts are coloured and showy like petals, e.g. Bougainvillea spectabilis (Nyctaginaceae), Euphorbia pulcherrima (Euphorbiaceae) etc.
(c) Scaly bracts-When bracts become thin and scale-like as seen in disc florets of capitulum inflorescence of Compositae.
(d) Spathy bract-Here the bracts are thick, large and boat-shaped and they either completely or partly surround the inflorescence, e. g. bracts of spadix inflorescence of Araceae, Palmae etc.
(e) Involucre of bracts-In this type, bracts are arranged in one or more whorls around the base of the flower or inflorescence, e.g. Helianthus annuus (Compositae), Daucus carota var. sativa (Umbelliferae) etc.
(f) Glumes, Lemmas etc.--These are dry, stiff and scaly bracts as seen in members of the families Gramineae and Cyperaceae. Glumes are non-flowering bracts while lemmas are flowering bracts carrying flowers at their axils.
(g) Epicalyx-It is a bracteole in nature, occurring at the base of the calyx whorl, as seen in Hibiscus rosa-sinensis and other members of the family Malvaceae.
(h) Cupule-When bracts or bracteoles grow together at the base of the flower and form a cup shaped hard body surrounding the fruit of some plants eg. Corylus sp.of Betulaceae.
Inflorescence: Inflorescence is the branch or branch-system bearing flowers "or the arrangement of flowers on the floral axis and is a branch system”.
The stalk of the
inflorescence is known as peduncle. The floral axis of an inflorescence bearing flowers is called rachis and the stalk of the individual flower is known as pedicel. Flowers having pedicels are called pedicellate and those without pedicels i.e. stalks are sessile. Sometimes the rachis instead of developing into a long axis, is condensed to form fleshy, flat or dilated structure called receptacle. The inflorescence axis (i.e. rachis) developing from an underground stem is known as scape. The small rachis of Gramineae i.e grass inflorescence produced beyond the flower is known as rachilla.
Inflorescences are mainly three types-
1)Indefinite or racemose inflorescence
2)Definite or cymose inflorescence
3)Mixed inflorescence.


Comments
Post a Comment