The stem
Kinds of Stem : Stems are generally rigid, firm and strong which enable plants to remain in an upright position, but there are plants having weak stems and which are not able to grow in an upright position.
Aerial stems may be (a) strong (erect) or (b) weak.
A. STRONG STEM :-Plants become erect and remain in an upright position due to the rigidity of the stem, as seen in herbs, shrubs and trees.
Read also-
Stem: Definition, characteristics, forms and surface of stems- digieduco
Roots: modified roots and functions of root-digieduco
Roots: Definition,characteristics, types and regions of roots-digieduco
Types of strong stem as seen in trees are as follows :
(a) Excurrent :-When the tree takes a pyramidal form due to the development of racemose branching it is known as excurrent e.g. species of Abies, Picea, Pinus (Gymnosperms), Polyalthia longifolia (Anonaceae) etc.
(b) Deliquescent :-When the tree takes a dome-shaped (more or less rounded) appearance due to cymose branching then it is known as deliquescent, e.g. Mangifera indica (Anacardiaceae).
(C) caudex- Tall erect unbranched stem is known as caudex. The stem bears leaves at its apex and annular scars of fallen leaf bases, e.g. cocos nucifera( palmae) , Borassus flabellifer(palmae) etc.
 |
| Culm of bamboo and flowering scape of onion |
(d)culm-Jointed stems are known as culm. In this case the nodes are solid and the intenodes are hollow, e.g. grasses such as Bambusa arundinacea (Gramineae). Scape :--In some monocotyledoneus plants the suppressed underground stem produces an erect unbranched aerial shoot which is known as scape. It comes out through the cluster of leaves and bears at its apex either a solitary flower or a cluster of flowers. The plant is defined as acaulescent, e.g. Polyanthes tuberosa (Amaryllidaceae), Allium cepa (Liliaceae), aroids, etc.
B. WEAK Stems :-Many stems are weak, they cannot maintain an upright position.
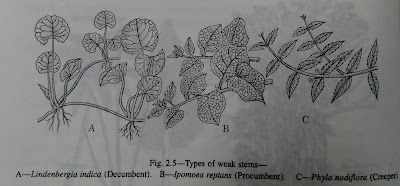
Types of weak stem -Weak stems are either (a) Trailer-trails over the surface of the ground without rooting at the nodes, or (b) Creeper-grows horizontally over the surface of the soil striking roots (arising from the nodes) at short distance or (c) Climber climbs up by supporting any other plant or object.
(a) Trailer or trailing plants :
(i) Procumbent or Prostrate-When the stem lies prostrate over the ground, its apex also lies flat over the surface e.g. Basella rubra (Chenopodiaceae), Evolvulus nummularius ,Ipomoea neptans (Convolvulaceae) etc.
ii) Decumbent- when the stem lies over the ground with the apex turned upwards e.g. Tridax procumbens( composite) , Lindenbergia indica ( scriphulariaceae)etc.
 |
| Types of weak stems |
(b) Creepers-When the plant grows horizontally over the surface of the soil and produces branches profusely and spreads out in all directions and gets rooted at each nodes, it is known as a creeper, e.g. Ipomoea batatas (Convolvulaccae), Cynodon dactyon(Gmmineac), Phyla nodiflora (Verbenaccae) etc.
(c) Climbers or Climbing plants :
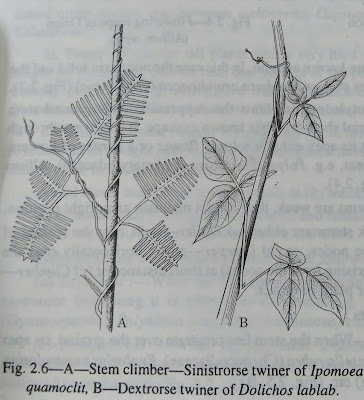
1. Stem climbers or Twiners- weak, long and slender stems of some plants like
Clitorea ternatea (Leguminosae Papilionaceae), Dioscorea alata (Dioscoreaceae), Quisqualis sp. (Combretaceae), Ipomoea quamoclit (Convolvulaceae) etc. climb up other plants or objects by twining round their own stem.
 |
| A- stem climber , B- dextrorse twiner |
Twiners are classified into two groups according to the direction of twining-
(i) Dextrorse-When the climbers twine clockwise or to the right then it is called dextrorse e.g. Dioscorea alata (Dioscoreaceae), Mikania scandens (Compositae), . Phaseolus sp. (Leguminpsae Papilionaceae), Dolichos lablab (Papilionaceae) etc.
(ii) Sinistrorse-When the climbers twine in anticlockwise or to the left then it is called sinistrorse e.g. Dioscorea bulbifera (Dioscoreaceae), Cliitorea ternatea (Leguminosae-Papilionaceae), Ipomoea quamoclit (Convolvulaceae), Convolvulus m. (Convolvulaceae) etc.
 |
| A- axillary stem tendril , B- apical stem tendril , C- leaf tendril |
2. Lianes-Long and woody perennial stem climbers which climb up tall forest trees. are called lianes. They climb up owing to the different growth and curvature of the stem e.g. Hiptage benghalensis (Malpighiaceae), Beaumontia grandiflora (Apocynaceae), Marsdenia (=Dregea) volubilis (Asclepiadaceae), Bauhinia vahlii (Legnmihosae Caesalpinaceae) etc.
 |
| A- stipular tendril, B- inflorescence axis tendril, C- tendrils of cucurbita sp |
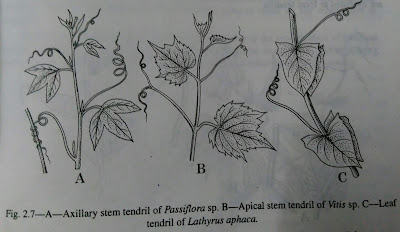
3. Tendril climbers-There are some plants which develop special type of climbing organs called tendrils. These are slender, spirally coiled, thread like structures which may be modifications of either branches or leaves or inflorescence stalk and are very sensitive
to contact. They help the plant to climb up any other plant or object. Different plant organs are modified to form tendrils.
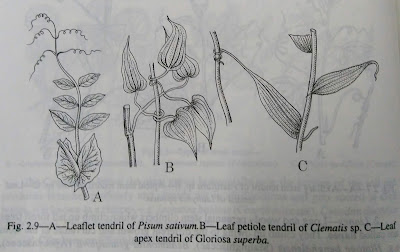 |
| A- leaflet tendril, B- leaf petiole tendril, C- leaf apex tendril |
(i) Tendrils may develop from the axil of leaf and are called stem tendrils ;either the axillary bud is modified into slender coily structure e.g. Passiflora sp. (Passifloraceae), or as in Vitis sp. (Vitaceae) the apical bud is modified into tendril.
(ii) Entire leaf is modified into tendril e.g. Lathyrus aphaca (LeguminosaePapilionaceae)
(iii) Terminal leaflets are modified into tendrils Pisum sativum (Leguminosae-Papilionaceae),
(iV) Apex of the leaf is modified into tendril e.g. Gloriosa superba (Liliaceae)
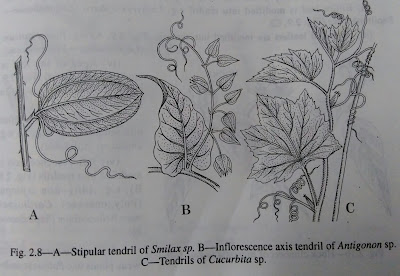
(v) Stipules are modified into tendrils e.g. Smilax sp. (Liliaceac).
(vi) Inflorescence axis is modified into tendrils e.g. Antigonon leptopus (Polygonaccae), Cardiospermum helicacabum (Sapindaoeae) etc.
4. Root climber-Several weak plants like Pothos scandens (Araceae), Piper betle (Piperaceae), Scindapsus officinalis (Araceae), Ficus pumila (Moraceae) etc. climb up suitable objects with the help of adventitious roots which develop from the nodes of the stem.
 |
| Hooks climbers |
5. Hook climbers :--In Artabotrys uncinatus (Anonaceae) curved hooks are developed from the flower stalks (pedicels) which help the plant to climb up any other plant or support. Hook-like structures are also formed due to the modification of terminal leaflets which also serve the climbing purpose e.g. Bignonia unguis-cati(Bignoniaceae); sometimes hooks are modified inflorescence axes, e.g. Anabotrys sp. (Anonaceae).
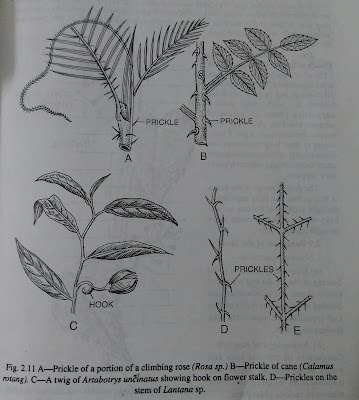 |
| A- pickle of a portion of a climbing rose, B- pickle of cane, C- a twig , D- pickles on the stem of lantana sp |
6. Leaf Climbers :-Leaf climbers are the climbing plants in which the leaf or pan of the leaf is modified into tendril and which act as climbing organ. The leaf-stalk i.e. petiole of Clematis sp. (Ranunculaceae) is sensitive
to contact and coil round any neighbouring object helping the plant to climb. In Nepenthes
Sp. (Nepenthaceae) the modified petiole often twists round the support like tendril holding the pitcher in vertical position.
7. Rambler or Scramblers :-Several plants have been found to climb neighbouring plants in forests with the help of prickles and thorns e.g. Bougainvillea Spectabilis (Nyctaginaceae), climbing rose, Calamus rotang (Palmae) etc. In Calamus rotang,. Iong slender whip-like stalk covered by prickles (hook-like) is produced from the leaf sheath this helps the plant to climb neighbouring plants or objects.
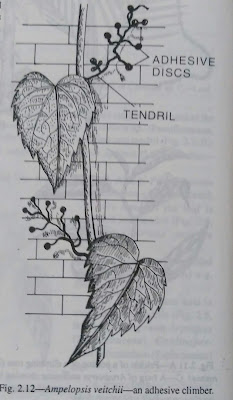 |
| Adhesive climber |
8. There is another type of climber called adhesive climber. These climbers are provided with adhesive discs to some of their organs, by means of such adhesive discs they may adhere to flat surfaces, e.g. Ampelopsis veitchii (Vitaceae). In this plant the adhesive discs are developed from the tendrils.









Comments
Post a Comment