Flower is a Modified shoot- That the
flower is a modified shoot or a branch in the very beginning can be revealed by the following facts :
1. AXIS NATURE OF THALAMUS-Flower consists of an axis known as
thalamus or torus.
(a) This axis bears modified floral leaves viz, sepals, petals, stamens and carpels. Generally the axis in a flower consists of short or suppressed internodes and nodes. But it is not always the case ; the axis is long in some flowers e.g. in Gynandropsis gynandra(Capparidaceae), Passiflora suberosa (Passifloraceae) etc. the internodes of the thalamus between corolla and androecium (called androphore) and between androecium and gynoecium (called gynophore) become enlarged with same whorled arrangement of stamens and carpels respectively ; so no doubt that the thalamus is axial in nature. In Capparis
sepiaria (Capparidaceae) the formation of gynophore only is also noted.
(b) Normally, the growth of the thalamus is checked by the carpels but in some cases like species of Pyrus (pear), Rosa (rose), etc., the thalamus had been found to undergo further upward growth having green stem with prickles and small foliage leaves beyond the gynoecium-this phenomenon is known as monstrous development or proliferation.
(c) In Polyalthia longifolia (Anonaceae), Michelia champaca (Magnoliaceae) eHoral the carpel bearing region of the thalamus elongates like the stem giving rise to an aggregate fruit.
2. LEAF NATURE OF FLORAL MEMBERS-That the floral leaves are modified leaves is proved in most cases by their leafy nature ; in many cases the sepals may assume typical leaf-like structure with veins and petal-like pigments e.g. Mussaenda frondosa (Rubiaceae).
The floral leaves also exhibit the same types of ptyxis and aestivation Le. prefoliation as those of foliage leaves.
In Michelia champaca, Magnolia sp. etc. of Magnoliaceae the floral leaves are both vertically and spirally arranged on long thalamus but in majority of flowers the floral phyllotaxy i.e. arrangement of floral leaves is whorled- this resembles the phyllotaxy of foliage leaves on the stem and branches.
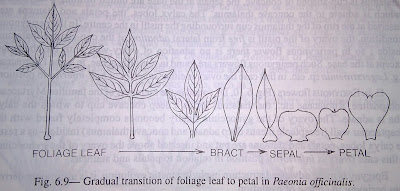
The leaf nature is also proved by the gradual transition of sepals to petals and petals to stamens as seen in flowers of Nymphaea sp. (Nymphaeaceae). The transition from leaves to sepals and from sepals to petals showing similar leafy structure is also noted in Paeonia sp. (Ranunculaceae).
In double flowers raised by horticultural skill e.g Rosa sp. (Rosaceae), Hibiscus rosa-sinensis (Malvaceae), the stamens are further remodifled into petals-so stamens are highly modified leaves.
In Canna sp. (Cannaceae), stamens are modified into petaloid staminodes. In Zinnia Sp. carpels are modified into sepaloid or petaloid structures.
That the carpel is also leafy in nature can be proved on examination of single carpel of pisum sativum (Papilionaceac) in which it is folded along its midrib to form a chamber (the ovary) containin g seeds. The elongated part of the carpellary leaf forms the style ; its extreme apex, the receptive spot for the pollen forms the stigma.
3. HOMOLOGY OF FLORAL BUDs-Floral buds like vegetative buds may be metamorphosed bulbils e.g. viviparous bulbils of Agave sp. (Agavaceae). Development and position of vegetative buds are also like those of floral buds i.e. axillary and terminal.



Comments
Post a Comment