There are two principal
methods of studying the internal structures of the
plant body, viz. (a) sectioning, i.e. cutting thin and uniform sections and (b) maceration techniques. Normally sections are cut by hand with the help of a sharp razor. Study of sections cut in more than one plane is necessary, specially for the complex structure of most plant parts. For the cylindrical plant part like axis (stem and root), sections are out both at right angles to the axis (called transverse section or cross section) and parallel to the axis (called longitudinal section).
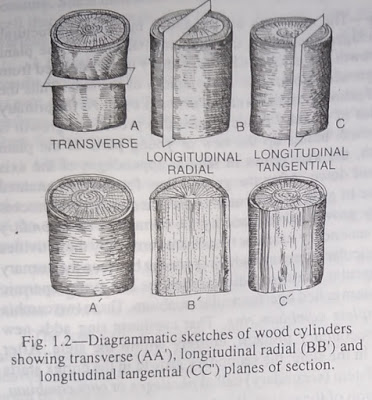
Of the longitudinal planes, there are two types viz., that dividing the axis radially is called radial plane (longitudinal radial section) and that at right angles to the radial plane is called tangential plane (longitudinal tangential section). For more detailed and critical study, the use of an apparatus known as microtome is desirable for cutting sections. With the aid of this instrument, a large number of thin serial sections may be cut, but before making sections by microtome the materials are to be killed, fixed in various fixatives and embedded in paraffin Which is a long-drawn process.
In maceration process the individual cell elements are freed from one another and thus they become isolated. The maceration of plant tissue is accomplished by the use of certain reagents that dissolve the intercellular substances lying between the cells and thus cause the separation of a piece of tissue into its component cells. In this process, the macerated materials, i.e. individual cells and other elements can be conveniently visualised as three-dimensional bodies against two-dimensional concept in sections.
Besides the above mentioned two methods, there are simple methods in studying plant materials ; these are whole mounts, scrape mounts, peel mounts etc. In peel mount some portions of plant materials like leaf epidermis is peeled off to study stomata and other epidermal cells, fleshy onion scale to study onion cellsetc. ; in whole mount process some lower plant groups like algae, fungi, prothali of fern plants i.e. cryptogams; hairs and trichomes of higher plants i.e. angiosperms etc. are mounted as a whole ; in scrape mounts, scraping of potato tuber to study starch grains is useful.

Comments
Post a Comment